Introduction
Remember that sinking feeling when you can’t find your phone? For a moment, your whole world—contacts, photos, private messages—feels like it’s vanished.
Now, imagine that feeling, but caused by someone who deliberately locked you out of everything. Your computer is frozen, your files are encrypted, and a mocking message demands payment to get your digital life back.
This isn’t a scene from a movie; it’s the reality of a cyberattack. And in 2025, it’s a risk that’s more relevant than ever.
But here’s the good news: you don’t need to be a tech wizard to protect yourself. This guide is your friendly, no-jargon map to the world of cybersecurity. We’ll break down what it really is, why it matters to you, and the simple steps you can take to build your digital armor. Let’s dive in.
Part 1: The Absolute Basics – Beyond the Hacker Stereotype
What is Cybersecurity, Really?
Let’s cut through the technical jargon. At its heart, cybersecurity is the practice of protecting internet-connected systems, including our devices, apps, and personal information, from digital attacks.
Think of it like this: your digital life has a front door, windows, and a mailbox. Cybersecurity is about putting strong locks on the door, installing alarms on the windows, and learning to spot junk mail that might contain a trick.
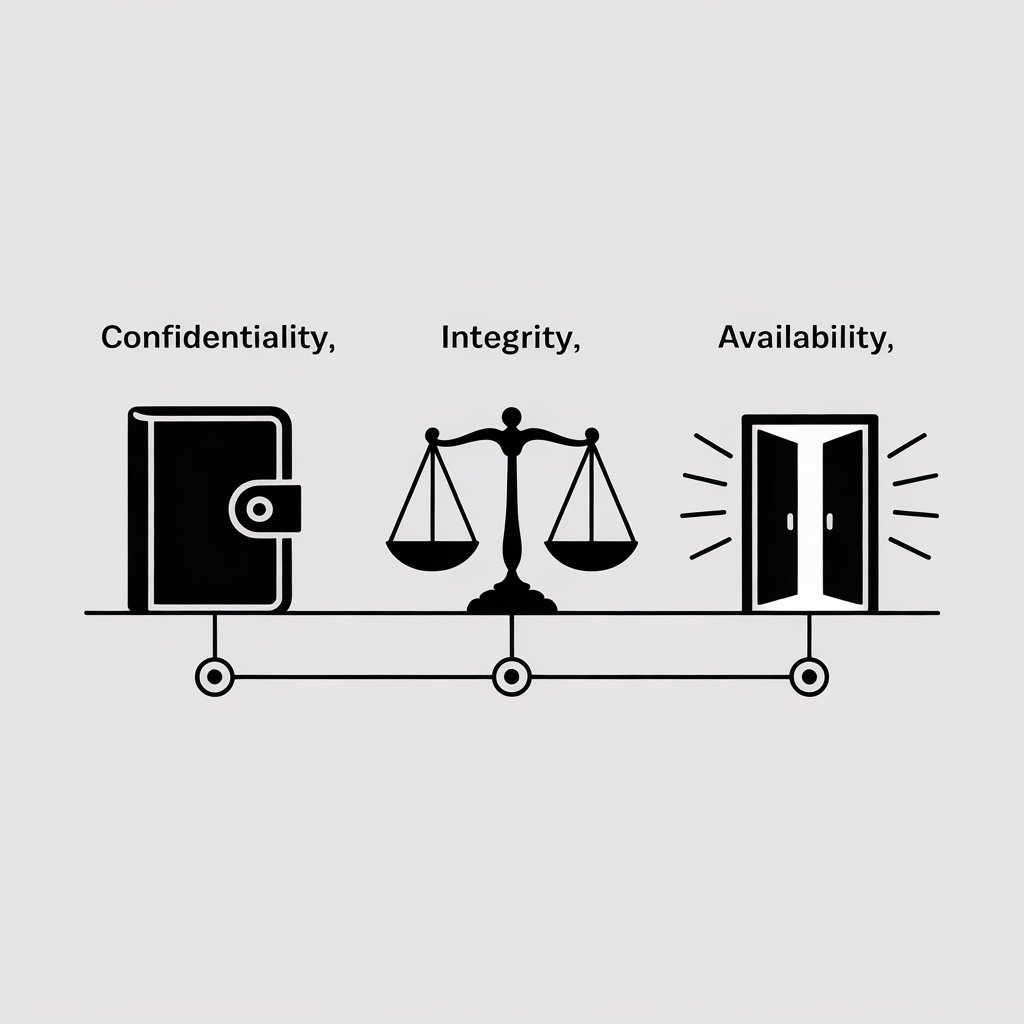
In the security world, this protection revolves around three core goals, often called the CIA Triad (no, not that CIA!):
- Confidentiality: This is about privacy. It ensures your data is seen only by people who are supposed to see it. Your private messages should stay private, and your bank details should be for your eyes only.
- Integrity: This is about trust and accuracy. It means ensuring your data is accurate and hasn’t been tampered with. You need to trust that the balance in your online banking app is correct and that a hacker hasn’t subtly altered an important document.
- Availability: This is about access. It means your systems and data are available when you need them. A hacker shouldn’t be able to shut down your favorite online service or lock you out of your own photo library.
Why Should You Care About Cybersecurity in 2025?
“It won’t happen to me.” It’s a comforting thought, but in 2025, it’s a risky one. Cybersecurity isn’t just for big corporations or government agencies anymore. It’s a personal necessity, and here’s why:
- The Rise of AI-Powered Attacks: The same artificial intelligence that writes poems and creates art is also being used by hackers. In 2025, AI can generate incredibly convincing phishing emails, create deepfake audio to impersonate your boss, and find vulnerabilities faster than ever. The “Nigerian prince” scams of the past have evolved into sophisticated, personalized attacks.
- Your Life is More Connected Than Ever (The Internet of Things): Look around your home. Your smart thermostat, your Wi-Fi baby monitor, your fitness watch, your voice assistant—these are all doors into your digital world. Each one is a potential entry point if not properly secured. In 2025, the number of these connected devices is staggering.
- Your Data is a Valuable Currency: Your email address, password, and even your shopping habits are worth real money on the dark web. Stolen data is bundled and sold, used for identity theft, or to launch more targeted attacks against you or your contacts.
- Remote Work is the New Normal: Many of us still work from home, at least part-time. Our home networks, often protected by a simple router password, have become extensions of the corporate office. A breach in your personal device can become a breach into your company’s sensitive data.
The bottom line? If you have an online presence, you have something worth protecting.
Part 2: The Digital Battlefield – Meet the Adversaries
To build a good defense, you need to know what you’re up against. Let’s meet the usual suspects.
Cyber Threats You Need to Know
1. Malware (Malicious Software)
This is an umbrella term for any software designed to harm or exploit a device.
- What it is: Think of malware as a germ for your computer. It’s a program that gets onto your device without your consent.
- Common Types:
- Virus: Attaches itself to a clean file and spreads, corrupting your system.
- Worm: Replicates itself to spread to other computers without needing a host file.
- Ransomware (The Big One in 2025): Locks your files or entire device and holds them hostage until you pay a ransom. It’s digital kidnapping for your data.
- Spyware: Secretly monitors your activity, capturing passwords and credit card numbers.
- How it affects you: Slows down your device, steals your information, or completely locks you out.
2. Phishing & Social Engineering
This is the art of human manipulation. Instead of attacking your software, they attack you.
- What it is: A scammer pretends to be someone you trust—your bank, your boss, a delivery company—to trick you into revealing passwords, clicking a malicious link, or downloading an infected file.
- The 2025 Twist: AI-Powered Phishing. Imagine getting a voicemail that sounds exactly like your CEO asking you to urgently buy gift cards. Or a video call from a “family member” in distress. Deepfake technology makes this possible, and it’s incredibly convincing.
- How it affects you: You willingly hand over the keys to your kingdom, thinking you’re just doing your job or helping someone out.
3. Password Attacks
Your password is the key to your digital front door. Hackers have several ways to copy it.
- What it is: Any method used to steal or guess your password.
- Common Methods:
- Brute Force Attack: Using automated software to try thousands of password combinations until one works.
- Credential Stuffing: Using username/password pairs stolen from one breach to try and log into other services (this is why reusing passwords is so dangerous!).
- How it affects you: A hacker gains direct, easy access to your accounts.
4. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
This one is like a digital eavesdropper.
- What it is: A hacker secretly intercepts and potentially alters the communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other.
- Simple Analogy: You think you’re having a private conversation with your bank teller, but a criminal is standing in the middle, listening to everything and even passing notes back and forth, pretending to be the teller.
- How it affects you: A hacker can steal your login details as you enter them, or alter a transaction so that money goes to their account instead of the intended one.
5. IoT-Based Attacks
Your smart devices can be turned against you.
- What it is: Hackers exploit weak security in Internet of Things devices like smart cameras, refrigerators, or DVR players.
- Example: A hacker gains access to a poorly secured smart home camera system, leading to a gross invasion of privacy. Or, they can recruit millions of these devices into a “botnet” to launch massive attacks on websites.
- How it affects you: Loss of privacy, or your devices being used as pawns in a larger cybercrime.
Part 3: Your First Line of Digital Defense – Your Cybersecurity Toolbelt
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t be. You don’t need to build a fortress overnight. Start with these foundational steps. They are simple, highly effective, and will make you safer than most people online.
How to Protect Yourself: Cybersecurity Basics for 2025
1. Fortify Your Passwords & Use a Manager
The era of using your pet’s name as a password is long over.
- Use a Password Manager. This is the single best thing you can do for your cybersecurity. Tools like Bitwarden, 1Password, or LastPass create, store, and auto-fill strong, unique passwords for every site you use. You only need to remember one master password. It’s a vault for your digital keys.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA/2FA) Everywhere. If a password is a key, MFA is a deadbolt. Even if a hacker gets your password, they can’t get in without this second step—usually a code from an app on your phone or a text message. Turn this on for your email, bank, and social media accounts today.
2. Become a Software Update Fanatic
Yes, those “update available” notifications are annoying. But they are your best friends.
- Why it matters: Software updates often include “patches” for newly discovered security holes. By not updating, you’re leaving those digital doors and windows wide open for hackers to walk through. Enable automatic updates on your operating system, web browsers, and apps whenever possible.
3. Think Before You Click: The Power of Healthy Skepticism
Your brain is your most powerful security tool.
- Spot the Phish: In 2025, phishing emails look real. But you can still spot the fakes.
- Check the Sender’s Address: Does it look slightly off? Is it from a public domain like
gmail.comor should it be from a company domain? - Hover Over Links: Before clicking, hover your mouse over any link to see the actual URL. Does it match the company’s real website?
- Beware of Urgency and Fear: Scammers create a sense of panic (“Your account will be closed in 24 hours!”) to make you act without thinking.
- Got an Odd Request? Verify Out-of-Band: If your “boss” emails asking for gift cards, call them on their known number or send a separate text to confirm.
- Check the Sender’s Address: Does it look slightly off? Is it from a public domain like
4. Secure Your Home Network
Your Wi-Fi router is the gateway to your digital home.
- Change the Default Password: When you set up your router, change the administrator password from the default one it came with. This is different from your Wi-Fi password!
- Use a Strong Wi-Fi Password: Use WPA3 encryption if your router supports it, and create a long, complex password for your network itself.
- Consider a VPN (Virtual Private Network): When using public Wi-Fi (at a coffee shop or airport), a VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it much harder for anyone to snoop on what you’re doing.
5. Back Up Your Data Regularly – The 3-2-1 Rule
This is your “undo” button for the worst-case scenario, like a ransomware attack.
- What is the 3-2-1 Rule?
- 3 copies of your data (your live data plus two backups).
- 2 different types of media (e.g., an external hard drive + a cloud service).
- 1 copy stored offsite (e.g., the cloud or a hard drive at a friend’s house).
If your computer is infected, you can simply wipe it clean and restore from your backup. The hackers get nothing, and you lose nothing.
Part 4: The Bigger Picture & Your Future
Is Cybersecurity a Good Career for You?

Maybe, after reading this, you’re not just scared—you’re intrigued. The good news is that the cybersecurity field is booming, with a 0% unemployment rate and a massive skills gap. Companies are desperately looking for talented people to help them defend against these threats.
You don’t necessarily need a computer science degree to start. The field values problem-solving skills, curiosity, and a knack for thinking like both a builder and a breaker.
- Beginner-Friendly Roles:
- Security Analyst: The front-line defender who monitors networks for threats.
- SOC Analyst (Security Operations Center): Works in a team to detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents.
- Vulnerability Analyst: Finds and helps patch weaknesses in software and systems.
- How to Start:
- Certifications: The CompTIA Security+ certification is the gold standard for entry-level cybersecurity knowledge.
- Online Learning: Platforms like Coursera, TryHackMe, and Cybrary offer fantastic beginner courses and hands-on labs.
- Get Hands-On: Set up a virtual lab on your own computer to practice safely.
Conclusion: Your Cybersecurity Journey Starts Now
We’ve covered a lot of ground, from the basic “what is cybersecurity” to the threats of 2025 and the simple steps you can take to fight back.
Remember, cybersecurity isn’t a destination; it’s a journey. It’s not about being perfectly secure—that’s impossible. It’s about being resilient. It’s about making it significantly harder for the bad guys to target you, and having a plan for when things go wrong.
So, don’t try to do everything at once. Start small.
Your first mission, should you choose to accept it: Go to your primary email account right now and turn on Multi-Factor Authentication. It will take you two minutes, and it will dramatically increase your security.
That’s it. One step at a time. You are no longer a passive target. You are now an active defender of your own digital life.
Welcome to the front lines. You’ve got this.